Get most out of bad welds
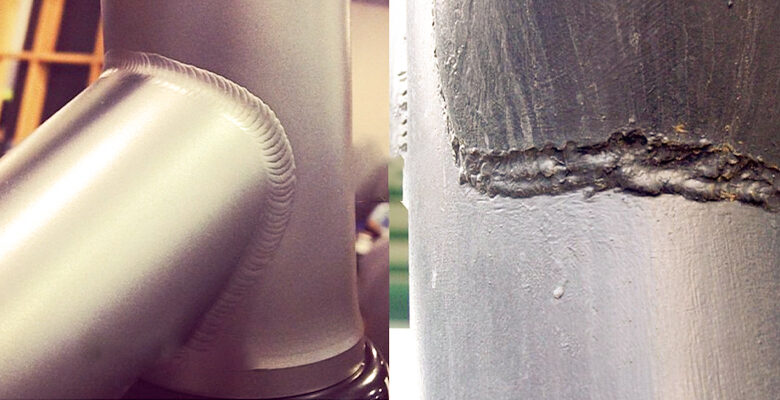

Are bad welds your welding projects not turning out as smooth and seamless as you’d like? Don’t fret! Even the most experienced welders encounter bad welds from time to time. But here’s the good news – there are ways to salvage those less-than-perfect joints and turn them into something remarkable. In this blog post, we’ll explore the world of bad welds, understanding their types, causes, and effects on different materials. We’ll also provide you with some valuable tips to improve your weld quality and guide you in repairing those pesky imperfections. So, grab your welding helmet and let’s dive right in!
Understanding Bad Welds
Understanding Bad Welds
When it comes to welding, not all joints are created equal. A bad weld is simply a joint that fails to meet the desired standards of quality and strength. It can occur due to various factors such as improper technique, inadequate preparation, or even using the wrong type of filler material.
One common type of bad weld is known as an undercut. This occurs when the weld bead doesn’t penetrate deep enough into the base metal, resulting in a weak joint that is prone to cracking under stress. Another issue you may encounter is porosity, which manifests as small holes or bubbles within the weld caused by contaminants like dirt or moisture.
A cold lap is another telltale sign of a bad weld. It happens when there’s insufficient fusion between two adjoining pieces of metal, leaving behind an incomplete bond that compromises overall integrity. Conversely, excessive heat can lead to distortion or warping in the welded structure.
To avoid these issues and achieve high-quality welds consistently, it’s crucial to understand their causes and take appropriate measures during each step of the welding process – from proper cleaning and preparation to selecting suitable equipment and using correct techniques.
By familiarizing yourself with different types of bad welds and their underlying reasons, you’ll be better equipped to identify potential pitfalls before they occur. This knowledge will empower you to make adjustments on-the-go or seek expert advice if needed.
Remember: even experienced professionals encounter bad welds at times; what sets them apart is their ability to recognize and rectify these flaws swiftly without compromising safety or structural integrity.
Stay tuned for our next blog section where we delve deeper into various types of bad welds!
Types of Bad Welds
Types of Bad Welds
When it comes to welding, a bad weld can have serious consequences. Understanding the different types of bad welds is crucial in order to identify and correct them effectively.
One common type of bad weld is called an undercut. This occurs when the welding material does not completely fuse with the base metal, resulting in a groove or depression along the edge of the joint. Undercuts weaken the overall strength of the welded joint and increase its susceptibility to cracking.
Another type of bad weld is known as porosity. Porosity happens when gas becomes trapped within the welded metal, causing small voids or bubbles to form. These voids compromise the structural integrity of the weld and can lead to leaks or failures under stress.
Overlap is yet another type of bad weld that occurs when there is insufficient penetration into one or both sides of a joint. This results in overlapping layers instead of a solid bond between materials, making it prone to separation under strain.
Incomplete fusion is another issue that arises during welding. When two pieces fail to fully merge together at their interface, weak spots are created where cracks may form over time due to stress on those areas.
We have spatter – tiny droplets expelled from molten metal during welding that can adhere onto nearby surfaces and cause aesthetic issues or even interfere with functionality if they accumulate excessively.
Understanding these different types of bad welds allows us to recognize their presence and take appropriate corrective measures before they result in larger problems down the line.
Causes of Bad Welds
Causes of Bad Welds
Poor welding techniques and lack of attention to detail can lead to bad welds. One common cause is improper preparation of the materials being welded. This includes not cleaning the surfaces properly, which can result in contaminants interfering with the welding process.
Another factor is using incorrect or insufficient electrode size for the job at hand. Inadequate heat input during welding can also lead to weak or incomplete fusion between the base metals, resulting in a faulty weld.
Furthermore, poor joint fit-up and alignment can contribute to bad welds. If the parts are not aligned correctly or if there are gaps between them, it becomes challenging to achieve a strong bond through welding.
Additionally, using incorrect parameters such as voltage and current settings on the welding machine can have adverse effects on weld quality. Inadequate shielding gas coverage or improper gas flow rates may also lead to defects like porosity or excessive spatter.
Lack of experience and skill on part of the welder plays a significant role in causing bad welds. It takes practice and knowledge to master proper technique and produce high-quality welds consistently.
By understanding these causes, one can take steps towards improving their welding skills and ensuring better results in future projects. Remember that proper training, careful preparation, appropriate equipment selection, and diligent attention to detail are key factors in achieving good quality welds.
Effects of Bad Welds on Different Materials
Effects of Bad Welds on Different Materials
When it comes to welding, the quality of the weld is crucial for ensuring a strong and durable joint. A bad weld can have serious consequences, especially when different materials are involved. Let’s take a look at how bad welds can affect different types of materials.
Metals such as steel and aluminum are commonly used in welding projects. A poor quality weld on these materials can lead to structural weakness and compromised integrity. The joint may not be able to withstand heavy loads or vibrations, posing safety risks in applications such as construction or automotive manufacturing.
For plastics, a bad weld can result in leaks or cracks, rendering the material useless for its intended purpose. Whether it’s PVC pipes or plastic components in electrical wiring systems, a faulty weld jeopardizes functionality and opens up possibilities for damage and failures.
In the case of composite materials like carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRPs), improper welding techniques can weaken the bond between layers and compromise their strength. This is particularly concerning in industries relying on CFRP structures like aerospace or sports equipment manufacturing.
Moreover, when dissimilar metals are welded together without proper consideration given to their compatibility, galvanic corrosion becomes a significant concern. This occurs when one metal corrodes more rapidly than the other due to electrochemical reactions at the interface of the joint.
To mitigate these effects caused by bad welds on different materials, attention must be paid to proper welding techniques and procedures that match each specific material type. It is essential to select appropriate filler metals compatible with both base metals during welding processes involving dissimilar metals.
Furthermore, regular inspection through non-destructive testing methods like visual examination or radiography should be carried out to identify any potential defect early on before they escalate into larger issues down the line.
Remember that investing time and effort into improving your welding skills will pay off immensely by avoiding costly repairs or even catastrophic failures caused by bad welds—ensuring the long-term strength, functionality, and safety of your creations.
By understanding
Tips to Improve Weld Quality
Tips to Improve Weld Quality
When it comes to welding, achieving a high-quality weld is essential for the strength and durability of the finished product. Here are some tips to help you improve your weld quality:
1. Prepare the surface: Before starting any welding project, make sure that the surfaces being joined are clean and free from rust, dirt, paint, or any other contaminants. Proper cleaning and preparation will ensure better adhesion of the filler metal.
2. Use proper technique: It’s important to use the correct welding technique for each application. This includes maintaining a steady hand, controlling heat input, and using appropriate travel speed.
3. Choose the right electrode: Selecting the right electrode for your specific needs can greatly impact weld quality. Factors such as base material type, thickness, and desired properties should be considered when choosing an electrode.
4. Control heat input: Excessive heat can lead to distortion or even burn-through in thinner materials while inadequate heat may result in poor fusion or incomplete penetration. Maintaining proper heat control is crucial for achieving a sound weld.
5. Monitor welding parameters: Keep a close eye on variables such as voltage setting, wire feed speed or amperage during welding process as they directly affect bead appearance and overall quality.
6. Conduct regular inspections: Inspecting your completed welds helps identify defects early on so that necessary adjustments can be made before proceeding further.
By following these tips consistently while practicing your welding skills over time; you’ll gradually see improvements in both visual appearance and structural integrity of your welded joints.
How to Repair a Bad Weld
When it comes to welding, a bad weld can happen even to the most experienced welder. Whether it’s due to a lack of skill, improper technique, or equipment failure, a bad weld can compromise the integrity and strength of the joint. But fear not! There are ways to repair these less-than-perfect welds and salvage your project.
The first step in repairing a bad weld is assessing the extent of the damage. Is it simply an aesthetic issue? Or does it affect the structural integrity? Once you’ve determined this, you can proceed with choosing an appropriate method for repair.
One common method for fixing bad welds is called grinding and re-welding. This involves carefully grinding away the faulty portion of the original weld and then applying new filler material to create a stronger bond. It requires precision and patience but can be effective in correcting mistakes.
Another option is known as “cold working.” This technique involves using specialized tools to reshape or manipulate the metal around the bad weld without generating heat. It’s often used when dealing with delicate materials or situations where excessive heat could further weaken the joint.
If all else fails, you may need to completely remove and redo the entire problematic section. This can be time-consuming and frustrating but ensures that you have a solid foundation for your project.
Remember, practice makes perfect when it comes to welding. Take every opportunity to hone your skills through training programs or by seeking guidance from more experienced professionals. By doing so, you’ll minimize future chances of encountering bad welds altogether!
Repairing a bad weld requires careful consideration of factors such as damage assessment, available methods like grinding/re-welding or cold working techniques,and ultimately deciding if complete removal is necessary.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing bad welds is essential for ensuring the quality and durability of welded structures. By identifying the types of bad welds, understanding their causes, and recognizing their effects on different materials, you can take proactive steps to improve weld quality.
Remember that prevention is always better than repair when it comes to welding. By implementing proper welding techniques, adhering to industry standards and guidelines, using high-quality equipment and materials, and maintaining a clean work environment, you can greatly reduce the occurrence of bad welds.
However, if a bad weld does occur despite your best efforts, it’s important to know how to properly repair it. Seek professional assistance or consult with experienced welders who can help you assess the situation accurately and provide appropriate solutions.
By staying informed about common welding issues and continuously improving your skills as a welder or fabricator, you can minimize the occurrence of bad welds in your projects. Remember that practice makes perfect in any craft – so keep honing your skills through training programs and hands-on experience.
With dedication and attention to detail, you’ll be able to consistently produce high-quality welded joints that are strong, reliable,and built-to-last.